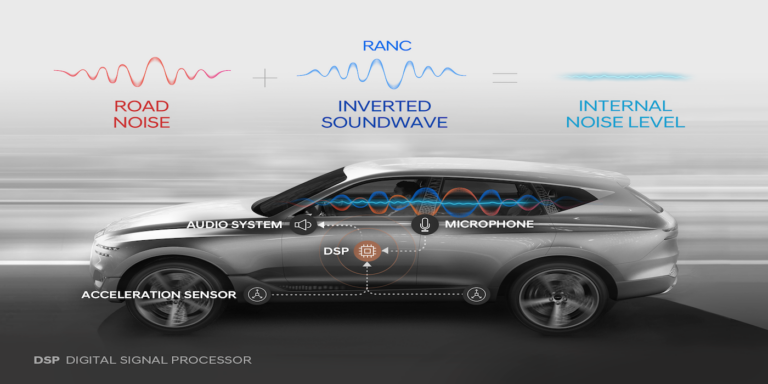
Hyundai Motor Group has developed a lightweight active noise-reduction system, which will make vehicle cabins quieter – a factor that will become more important as internal combustion engines are phased out. Named Road Noise Active Noise Control (RANC), the system builds on the group’s current active noise control (ANC) technology, which actively reduces noise by emitting soundwaves inverted to incoming noise. ANC is a software-driven technology that analyses the in-cabin sound to decrease engine and road noise, versus than the passive method of blocking noise through sound insulation.
Hyundai’s previous noise insulation methods involved sound insulation and dynamic dampers, which had a weight penalty and also failed to block any buzzing infrasound entirely. In contrast ANC, which is already available in some Hyundai Motor Group vehicles, uses much lighter parts such as microphones and controllers to control the noise and reduce infrasound more efficiently.
However, due to the limitations of noise measurement and analysis technology, the existing ANC is only effective when noise is constant and the occurrence of the noise predictable, meaning it was most commonly used to counteract constant engine noise. Given that it only takes about 0.009 of a second for road or engine noise to reach the passenger’s ears, the current technology is limited.
However, RANC technology, claimed by Hyundai Motor Group to be the first technology of its kind, is better able to reduce cabin noise. The system analyses various types of noise in real-time and produces inverted soundwaves. For example, there are different types of road noises that the new technology can process, such as resonant sounds created between tyres and wheels, or road noise.
Using an acceleration sensor, RANC calculates the vibration from the road to the car, and the control computer then analyses road noise. As the system’s computation and signal transfer speeds are optimised, it only takes 0.002 seconds to analyse the noise and produce an inverted soundwave, which is generated by the DSP (digital signal processor). The microphone constantly monitors the road noise cancellation status, and sends the information to the DSP. RANC is able to conduct accurate noise analysis and rapid computation to separately counteract road noise at the driver’s seat, the passenger seat and rear seats.
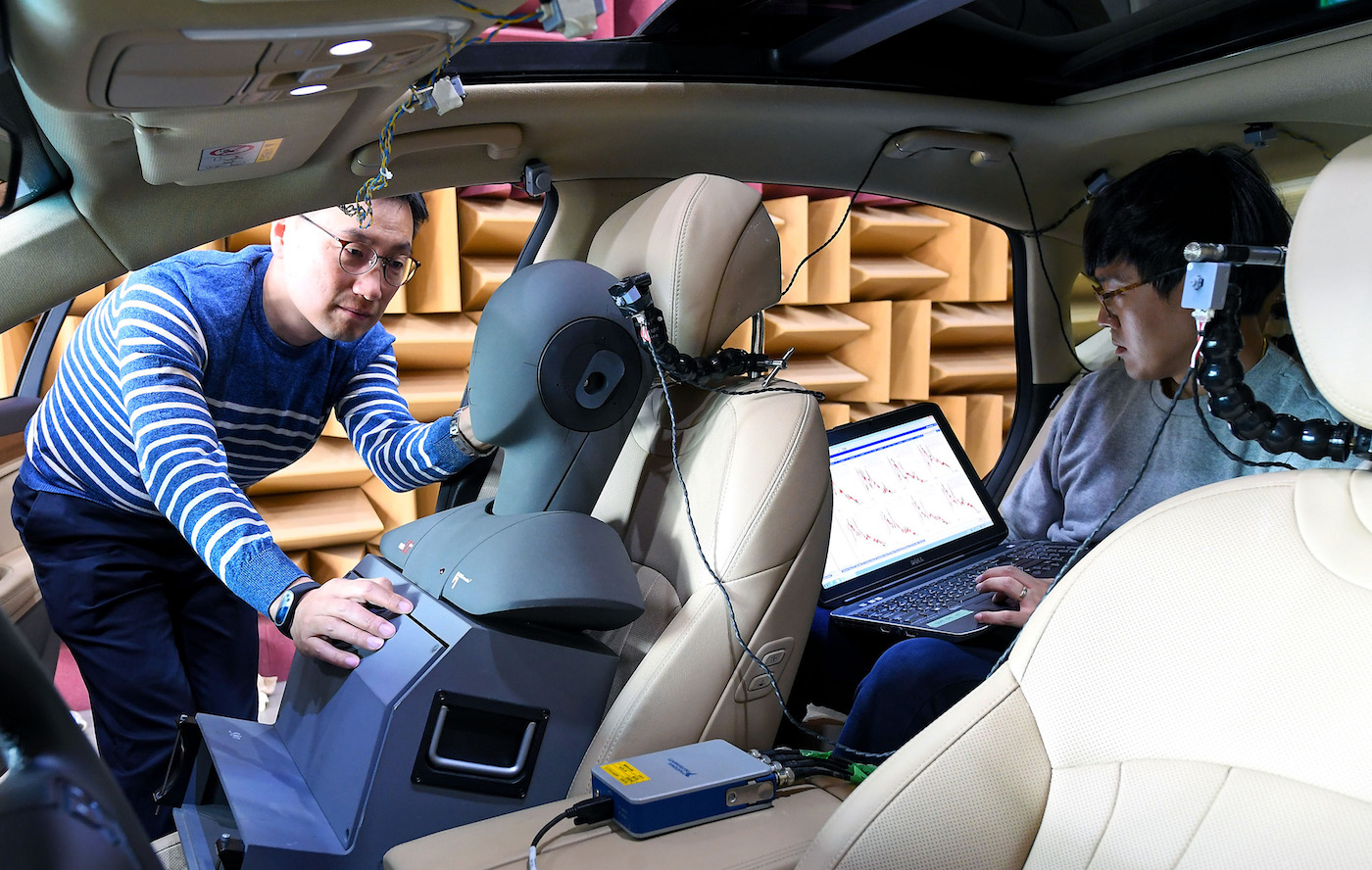

Based on tests evaluating road surface, vehicle speed, and different seating positions, tests have shown that RANC is able to reduce in-cabin noise by 3dB – roughly half the noise level experienced without RANC. The system also means that Hyundai Motor Group can potentially decrease the amount of unsprung weight in a vehicle, using fewer sound-insulating parts and dampers.
The group’s R&D department has spent six years getting RANC ready for mass production, ahead of its launch with an upcoming Genesis model. The pre-production phase involving an open innovation between industry and academia, with participation by the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology, WeAcom, ARE, BurnYoung and others. The mass production phase was also carried out with global car audio company, Harman. Hyundai Motor Group has completed domestic and American patent applications pertaining to the location of sensors and signal selection method, which are the core technologies of RANC.
“RANC is a remarkable technology which takes existing NVH technology to the next level,” said Gangdeok Lee, a research fellow at Hyundai Motor Group’s NVH research lab, “We will continue to take the leading position of NVH technology and deliver the highest level of quietness to customers.”