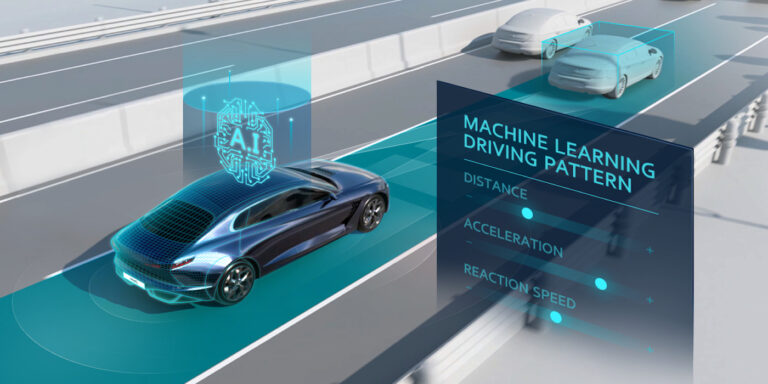
Hyundai has independently developed what it says is the world’s first machine learning-based smart cruise control (SCC-ML) technology, a system that incorporates the driver’s patterns into its self-driving behaviour, to create a travel experience suitable for the individual driver. The technology incorporates artificial intelligence (AI) within the advanced driver assistance system (ADAS), and is planned for implementation in future Hyundai Motor Group vehicles.
Smart cruise control (SCC) enables self-driving features and is a core technology for ADAS, maintaining an appropriate distance from the vehicle ahead while travelling at the speed selected by the driver. The SCC-ML combines AI and SCC into a system that learns the driver’s patterns and habits on its own, and through machine learning, can then autonomously drive in the same patterns as the driver.
“The SCC-ML improves upon the intelligence of the previous ADAS technology to dramatically improve the practicality of semi-autonomous features,” said Woongjun Jang, VP at Hyundai Motor Group. “Hyundai Motor Group will continue the development efforts on innovative AI technologies to lead the industry in the field of autonomous driving.”
In order to operate current SCC systems, the driver manually adjusts driving patterns, such as the distance from the preceding vehicle and acceleration. As good as the systems are, they are not able to meticulously fine-tune the settings to accommodate the driver’s individual preferences.
For example, a driver may accelerate differently in high speed, mid speed and low-speed environments, depending on the circumstances. Therefore, when SCC is activated, the vehicle may operate in a different way to their preferences, and when drivers sense this difference they may feel anxious and thus reluctant to use the technology. However, the detailed fine-tuning enabled by machine-learning technology makes the vehicle’s operation closer to their own individual driving style.

So how does SCC-ML work? First, sensors such as the front camera and radar constantly acquire driving information and send it to the centralised computer, which then extracts relevant details from the gathered information to identify the driver’s patterns. An artificial intelligence technology – the machine-learning algorithm – is applied during this process.
The driving pattern can be categorised into three parts: distance from preceding vehicles, acceleration patterns, and responsiveness (how quickly the driver responds to driving conditions). Driving conditions and speeds are also considered.
For instance, the system would maintain a short distance from the preceding vehicle during slow city driving and further away when driving in the overtaking lane of a freeway. Taking into account these various conditions, SCC-ML makes an analysis to distinguish over 10,000 patterns, and this flexible SCC technology can adapt to any driver’s patterns. The driving pattern information is regularly updated with sensors, reflecting the driver’s latest driving style. In addition, SCC-ML is programmed specifically to avoid learning unsafe driving patterns.
According to Hyundai, SCC-ML achieves Level 2.5 self-driving. which is useful for upcoming highway driving assist systems that feature automatic lane-change assistance.